Creating Environments
After creating a system in the Metadata Manager, you can create environments under the system. An environment can be created for different database types and flat files by fulfilling prerequisites and providing the connection parameters.
- Go to Application Menu > Data Catalog > Metadata Manager > Explore.
- In the Data Catalog pane, right-click a system.
- Click New Environment.
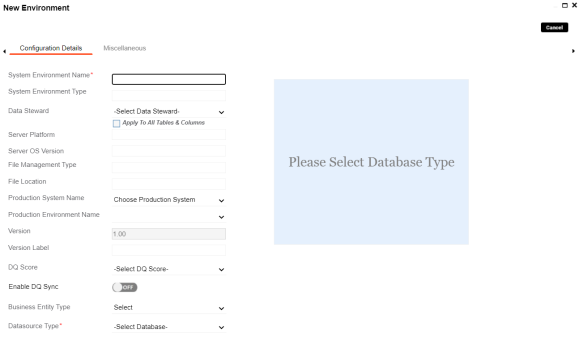
- Enter appropriate values in the fields. Fields marked with a red asterisk are mandatory. Refer to the following table for field descriptions.
- - (hyphen)
- ( (opening parenthesis)
- ) (closing parenthesis)
- / (slash)
- Click
 to test the connection.
to test the connection. - Click the Miscellaneous tab and enter appropriate values in the fields. Fields marked with a red asterisk are mandatory. Refer to the following table for field descriptions.
- Click Save and Exit.
The available options appear.
The New Environment page appears.
|
Field Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
System Environment Name |
Specifies the unique name of the environment. For example, EDW-Test. The following special characters are supported in an environment name: For more information on naming conventions, refer to the Best Practices section. |
|
System Environment Type |
Specifies the type of the environment. For example, development, test, or production. |
|
Data Steward |
Specifies the name of the data steward responsible for the environment. For example, Jane Doe. Users assigned with the Legacy Data Steward role appear as drop down options. You can assign this role to a user in the Resource Manager. To assign data steward, select a data steward from the drop down options.. |
|
Server Platform |
Specifies the server platform of the environment. For example, Windows. |
|
Server OS Version |
Specifies the OS version of the environment's server. For example, Windows Server 2012 R2. |
|
File Management Type |
Specifies the file management system (if the environment is a file-based source). For example, MS Excel. |
|
File Location |
Specifies a file path (if the environment is a file-based source). For example, C:\Users\Jane Doe\erwin\Mike - Target System |
|
Production System Name |
Specifies the system name being associated with the environment as the production system. For example, Enterprise Data Warehouse. |
|
Production Environment Name |
Specifies the environment name being associated with the environment as the production environment. For example, EDW-PRD. |
|
Version Label |
Specifies the version label of the environment to track change history. For example, Alpha. For more information on configuring version display, refer to the Configuring Version Display of the Environments topic. |
|
DQ Score |
Specifies the overall data quality score of the environment. For example, High (7-8). For more information on configuring DQ scores, refer to the Configuring Data Profiling and DQ Scores topic. |
|
Enable DQ Sync |
Specifies whether to sync data quality analysis results from DQLabs. To view data quality analysis, ensure that you have configured DQLabs connection setting in erwin DI. For more information, refer to the Configuring DQLabs topic.
Data quality analysis is available for environments using Oracle, Salesforce, Snowflake, MySQL, MSSQL, Hadoop, and PostgreSQL database types. |
|
Business Entity Type |
Specifies the database type of business entity. |
|
Database Type |
Specifies the database type. For example, Sql Server. Select the type of database from where you wish to scan metadata. Depending upon your choice of database type you need to provide additional fields (connection parameters) appearing on the right hand side. There are no additional fields for MS Excel File, and XSD. |
If the connection with database is established successfully then a success message pops up.
|
Field Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Sensitive Data Indicator Classification |
Specifies the sensitivity data indicator (SDI) classification of the environment. Also, you can add multiple classifications to the environment. For example, PHI, Confidential. For more information on configuring SDI classifications, refer to the Configuring Sensitivity Classifications topic. |
|
Intended Use Description |
Specifies the description about the objective of the environment. For example: The environment contains the source metadata for the data integration project. |
|
Environments Notes |
Specifies relevant notes about the environment. For example: The environment uses Sql Server as database to scan the metadata. |
|
Approval Instructions |
Specifies any instructions for the environment's approval. For example: The environment must contain 50 tables from erwin DI database. |
A new environment is created and stored in the environment tree.
Once an environment is created, you can scan source or target metadata from the database type.
Different database types have different prerequisites and connection parameters:
|
Copyright © 2022 Quest Software Inc. |